Absorption and radiation by land and water paint a captivating narrative of energy exchange and its profound impact on our planet. This intricate interplay shapes the very essence of our environment, influencing temperatures, driving the water cycle, and shaping land and water management practices.
Delving into this subject, we uncover the mechanisms by which solar energy is absorbed and radiated by different land and water surfaces, exploring the factors that govern these processes. We then examine the consequences of these energy exchanges, witnessing their influence on local and global climate patterns and their role in the delicate balance of the water cycle.
Absorption and Radiation of Solar Energy
Solar energy is absorbed and radiated by land and water in different ways. Land surfaces, such as soil and vegetation, absorb more solar energy than water surfaces. This is because land has a higher albedo, which means it reflects less solar energy back into space.
Water, on the other hand, has a lower albedo and reflects more solar energy back into space.
Factors Influencing Absorption and Radiation, Absorption and radiation by land and water
- Surface color: Darker surfaces absorb more solar energy than lighter surfaces.
- Surface texture: Rough surfaces absorb more solar energy than smooth surfaces.
- Angle of the sun: The angle at which the sun’s rays hit a surface affects the amount of solar energy that is absorbed.
- Cloud cover: Clouds can block the sun’s rays and reduce the amount of solar energy that is absorbed by land and water.
Impact of Absorption and Radiation on Land and Water Temperatures
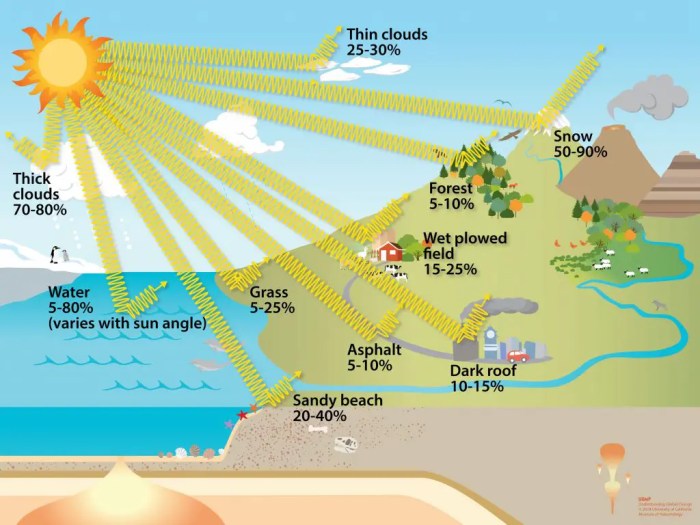
The absorption and radiation of solar energy by land and water affects their temperatures. Land surfaces heat up more quickly than water surfaces because they absorb more solar energy. This is why land is often warmer than water during the day.
At night, land surfaces cool down more quickly than water surfaces because they radiate more heat back into space.
Temperature Differences
The temperature differences between land and water surfaces can have a significant impact on local and global climate patterns. For example, the warm air over land can rise and create thunderstorms, while the cool air over water can help to stabilize the atmosphere.
Role of Absorption and Radiation in the Water Cycle: Absorption And Radiation By Land And Water
The absorption and radiation of solar energy by land and water play a key role in the water cycle. Solar energy evaporates water from land and water surfaces, which then condenses to form clouds. The clouds eventually release the water as precipitation.
Evaporation, Condensation, and Precipitation
- Evaporation: The process by which water changes from a liquid to a gas.
- Condensation: The process by which water vapor changes from a gas to a liquid.
- Precipitation: The process by which water falls from the sky in the form of rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
The amount of solar energy that is absorbed by land and water surfaces can affect the rate of evaporation, condensation, and precipitation.
Applications of Absorption and Radiation in Land and Water Management
Understanding absorption and radiation can be applied to improve land and water management practices. For example, farmers can use this knowledge to select crops that are adapted to the local climate and to schedule irrigation accordingly.
Water Conservation
By understanding how solar energy is absorbed and radiated by land and water, we can develop strategies to conserve water. For example, we can plant trees to shade water bodies and reduce evaporation.
Erosion Control
Solar energy can also be used to control erosion. By planting vegetation on slopes, we can help to hold the soil in place and reduce erosion.
Crop Growth
The absorption and radiation of solar energy can also be used to enhance crop growth. By selecting crops that are adapted to the local climate and by scheduling irrigation accordingly, farmers can maximize crop yields.
Clarifying Questions
How does absorption differ between land and water?
Land surfaces generally absorb more solar energy than water bodies due to their darker coloration and higher thermal capacity.
What factors influence the radiation of heat by land and water?
Factors such as surface temperature, emissivity, and atmospheric conditions play a role in determining the amount of heat radiated by land and water.
How does absorption and radiation affect local climate patterns?
Differences in absorption and radiation rates between land and water can create temperature gradients that drive local wind patterns and influence precipitation.